pulmonology
Pulmonology pertains to identifying and treating all ailments affecting the respiratory system, which comprises the nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, alveoli, lungs, and respiratory muscles. In essence, this field addresses disorders impacting the lungs, airways, and related muscles.
Pulmonology includes a diverse array of respiratory issues and lung illnesses. Below are some of the most prevalent examples:
Asthma:
Asthma is a persistent inflammatory condition that impacts the airways, leading to symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, a sensation of tightness in the chest, and difficulty breathing. Effective management, incorporating inhaled treatments, can assist in regulating asthma symptoms and reducing the likelihood of flare-ups.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD):
COPD comprises a group of progressive lung disorders, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis, which hinder breathing. Smoking is the primary risk factor for COPD, and treatment typically involves a combination of medications, oxygen therapy, and lifestyle changes.
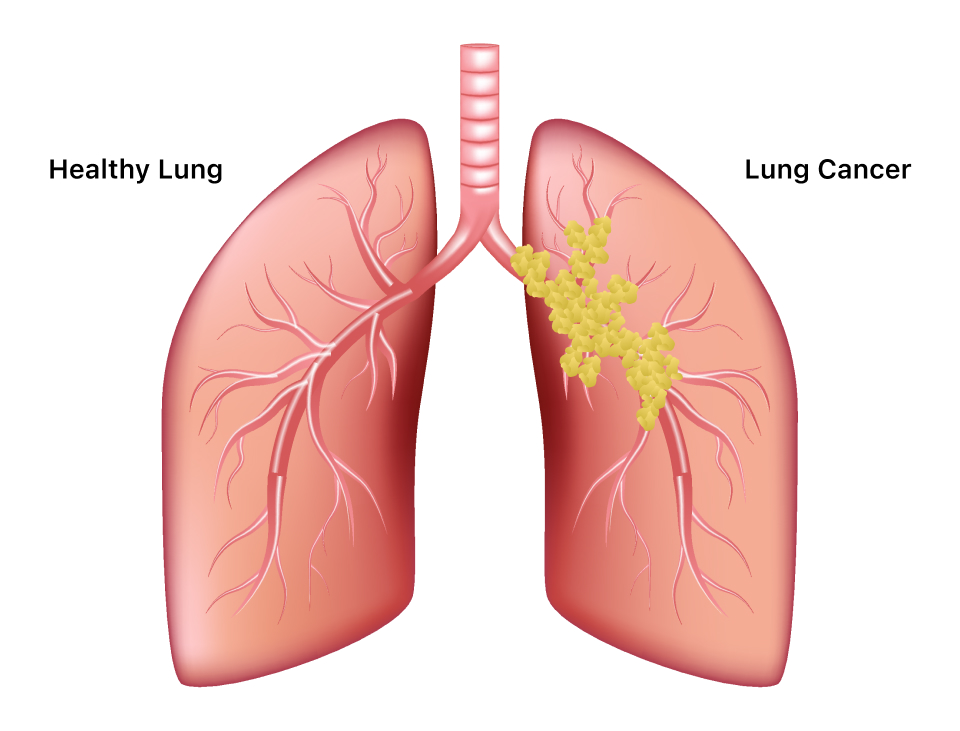
Lung Cancer:
Lung cancer is a serious health condition affecting various regions of the lung. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment strategies are essential for enhancing prognoses. Treatment options may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies.
Interstitial Lung Diseases:
Interstitial lung diseases encompass a range of conditions that lead to inflammation and scarring in lung tissue, which can make breathing challenging. Examples of these diseases include idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis.
Respiratory Infections:
Respiratory infections, including pneumonia, bronchitis, and influenza, can adversely impact lung health and functionality. Treatment may involve antibiotics, antiviral medications, and supportive care.
Sleep-Disordered Breathing:
Disorders such as sleep apnea, which result in interrupted breathing during sleep, can have a considerable effect on respiratory health and overall well-being. Treatment frequently includes the use of specialized devices, like continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines.